Analysis of internal corrosion in subsea oil pipeline
M.N. Ilman - Gadjah Mada University
(in lingua inglese)
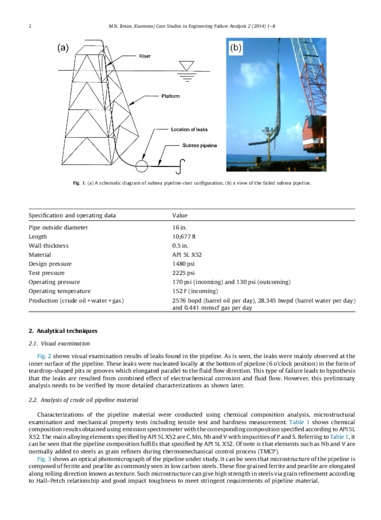
Based on visual analysis, it can be seen that the leaks are in the form of teardrop shaped pits or grooves at the bottom of the pipeline (6 o’clock position) where water layers preferentially form. The absence of scales or deposits around the grooves suggest that the pipeline is locally attacked by flow-induced corrosion. Such corrosion initially produces brittle scales or rusts on the pipe surface exposed to the fluid. These scales act as barrier between the metal surface and the fluid so that further corrosion penetration is inhibited. Subsequently, the fluid flow causes the erosion process and the scales or corrosion products are periodically scoured from the exposed surface hence increasing corrosion rate along the flow direction.
Fonte: Articolo Case Studies in Engineering Failure Analysis, 2013
Settori: Manutenzione meccanica, Meccanica
- Savino Barbera
- Valentina Zaninetti
- Simona Elena Silingardi
- Mohamed Hanafy El-Sayed
 English
English